
Calcium reacts easily with water and acids to form various compounds as well (e.g. It can also be burned or combusted in air which results in a very bright light and a nitride product. When it comes in contact with air, it corrodes (or tarnishes) to form a dark calcium oxide (CaO) and nitride (Ca3N2) coating (which prevents it from further corrosion).
#CA ELEMENT BOND FULL#
It is inclined to donate those electrons, forming a chemical bond, in order to achieve a full octet. Boiling Point: 1484 ☌ = 2703 ☏ = 1757 KĬalcium is a very reactive metal due to its two valence electrons.You can actually cut calcium metal with a knife (though it’s not a very easy task!) Physical PropertiesĪt room temperature and pressure, calcium exists as a ductile silvery white metal that can be easily cut or scratched. Like most metals, calcium is a relatively good conductor of heat and electricity. Calcium is classified as a solid and metal.
#CA ELEMENT BOND FREE#
mouth, esophagus, stomach).Ĭalcium does not occur as a free element in nature (because it is so reactive), but it can be found in many minerals, like limestone rock. However, calcium metal, because it reacts so violently with water, causes severe irritation when it comes into contact with moist parts of the body (e.g. As you know, calcium is an integral part to our bodies, so it is not surprising that its compounds are non-toxic to living organisms. It corrodes rapidly in air and reacts with water. Number of Neutrons : 20Īt room temperature elemental calcium is a soft (easily scratched), silvery white solid.“Earth” is an old term used by early chemists to describe nonmetallic compounds that are not soluble in water and are poor conductors of heat, which describes the oxides of the alkaline earth metals. The word “earth” is included as part of the description given to their oxides.

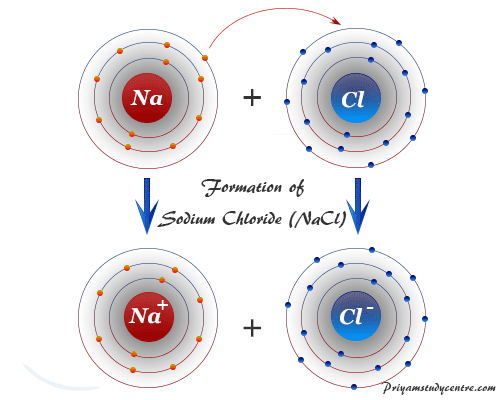
Elements in Group 2 are referred to as the alkaline earth metals.Īlkaline earth metals are called so because they form alkaline (basic) solutions when they react with water (by forming hydroxides). Calcium is the third element in Group 2 of the periodic table, appearing after Calcium and its compounds are used for cement and plaster in building applications, in water treatment, and in the chemical industry.Ĭalcium’s name is derived from the Latin word “calx,” meaning “lime.” This stems from the fact that lime (calcium oxide) is mainly made of calcium. On the left side of the periodic table, near the other alkali and alkaline earth “Calcium” by Jurii has not been altered and is licensed under CC Attribution 3.0 UnportedĬalcium is silvery white solid at room temperature and pressure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
